How It Works: Perfect Air Flow
Understanding Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality (IAQ) refers to the condition of the air within and around buildings, especially as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants. Good IAQ involves controlling pollutants from indoor sources, maintaining adequate ventilation, and managing humidity levels. Key factors influencing IAQ include chemical pollutants, particulates, and microbial contaminants.
Sources of Indoor Air Pollutants
Common indoor air pollutants include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, radon, and particulate matter. These pollutants can originate from various sources such as building materials, furnishings, cleaning products, and outdoor air infiltration. Ensuring good IAQ involves identifying and mitigating these sources through careful selection of materials and effective building practices.
Health Implications of Poor IAQ
Poor IAQ can lead to a range of health issues, from short-term effects like headaches, dizziness, and fatigue to long-term consequences such as respiratory diseases, heart disease, and cancer. Particularly vulnerable groups include children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Maintaining high IAQ is essential for creating healthy indoor environments that promote overall well-being and productivity.
Measuring and Improving IAQ
IAQ is measured using various parameters, including levels of VOCs, particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), carbon dioxide (CO2), and humidity. Improving IAQ involves increasing ventilation rates, using air purifiers, implementing source control measures, and selecting low-emission materials and products. Regular monitoring and maintenance are also critical in sustaining good IAQ over time.


Airflow and How It Works
Importance of Airflow in Indoor Spaces
Airflow refers to the movement of air within a space, crucial for maintaining good IAQ by dispersing pollutants and bringing in fresh air. Proper airflow ensures that contaminants are diluted and removed from the indoor environment, reducing the concentration of harmful substances.
Air Exchange Rate
The air exchange rate is a measure of how often the air within a space is replaced with outdoor air. It is typically measured in air changes per hour (ACH). For example, the average meeting room has an air exchange rate of 6-8 times per hour. Higher air exchange rates improve IAQ by continuously introducing fresh air and removing stale air.
Enhanced Airflow in Modern Pods
Advanced pods are designed to achieve higher air exchange rates, ensuring better ventilation and air quality. For instance, some pods offer an air exchange rate of up to 106 times per hour, which is 17 times more effective than a typical meeting room. This high rate of air circulation helps maintain optimal air quality by reducing the buildup of pollutants and maintaining comfortable CO2 levels.
Mechanisms of Airflow
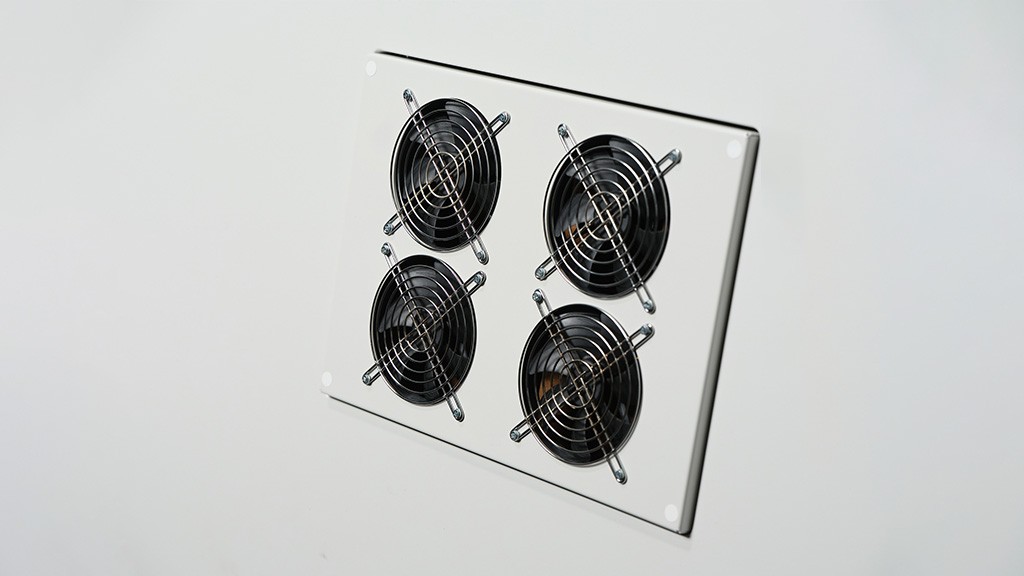
Airflow in indoor spaces can be achieved through natural ventilation (windows, vents) and mechanical ventilation systems (HVAC). Modern pods often incorporate both, with additional features like double redundancy fans that ensure continuous air movement even if one system fails. Airflow direction can also be adjusted, allowing for top-down or bottom-up ventilation based on user preference.
Benefits of Good Airflow
Good airflow not only enhances IAQ but also contributes to thermal comfort, reduces humidity levels, and prevents the growth of mold and mildew. Effective ventilation systems are crucial for creating healthy, comfortable, and productive indoor environments.